Revolutionizing aerospace design with 3D printing
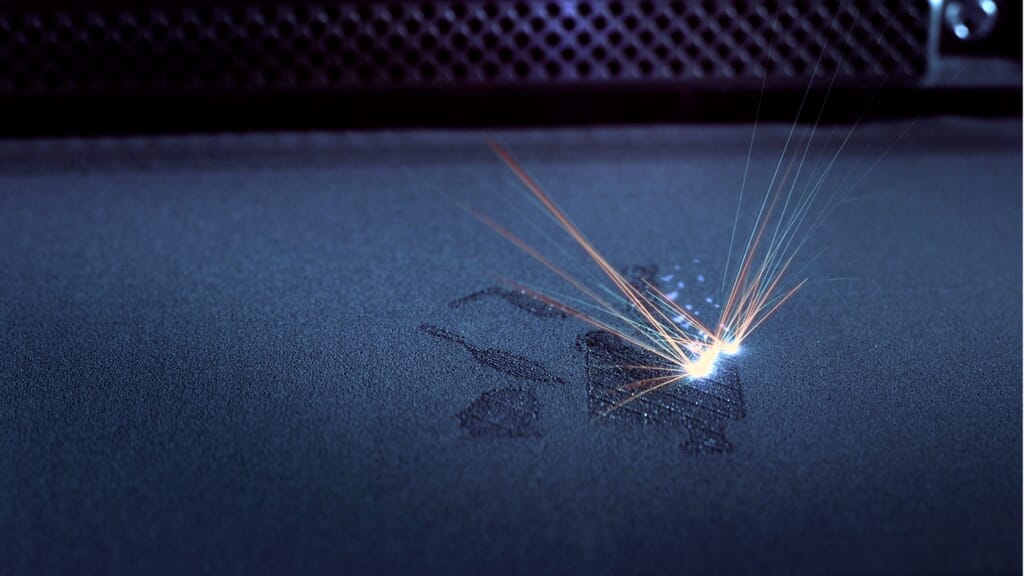
Additive manufacturing for aerospace has redefined how the industry approaches modern challenges in space exploration. AnyShape utilizes cutting-edge 3D printing technologies to produce intricate designs that optimize flight efficiency, reduce weight, and boost performance. From rocket thrusters to RF antennae, our additive manufacturing processes allow us to craft high-precision metal parts with significantly reduced lead times. Engineers can now iterate designs in a matter of days, not weeks, enabling rapid prototyping and real-time adjustments.
Mission-critical components for modern space exploration
Reliability is a non-negotiable in today’s rapidly-evolving aerospace industry. AnyShape manufactures mission-critical components that are designed to endure the most extreme conditions; from satellite systems exposed to intense radiation, to complex spacecraft parts destined for manned missions. Our aerospace parts are built for peak performance under the most intense flight conditions, including traveling at 4.9 miles per second under 3G vibrations, enabling your spacecraft to fly farther and faster.

Accelerating aerospace development with additive manufacturing
In an industry where speed is crucial, additive manufacturing is paving the way for faster production and innovation. Traditional manufacturing methods for aerospace components are extremely slow and costly, whereas AnyShape’s advanced 3D printing delivers rapid iteration, testing, and validation. By removing the hurdles associated with traditional tooling, we enable leading aerospace companies to reduce costs, shorten development timelines, and bring pioneering technologies to market much quicker.
Lightweight solutions for enhanced flight performance
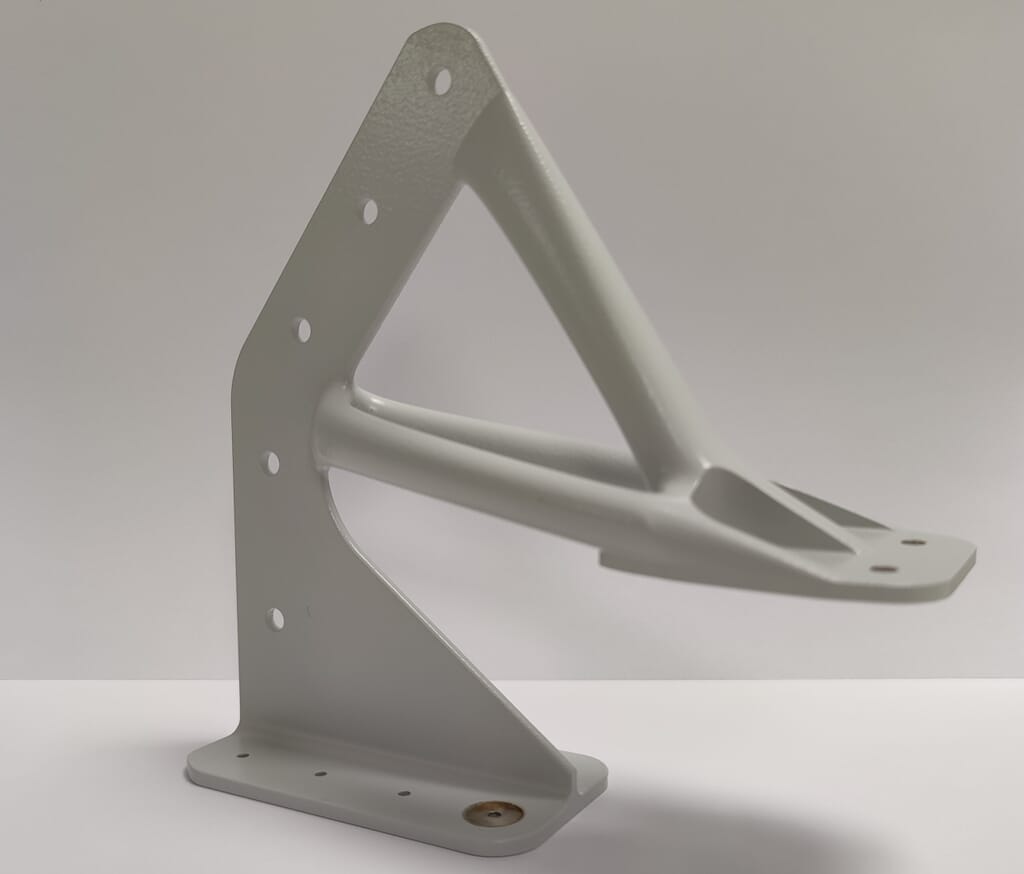
Weight reduction is a critical factor in aerospace design and manufacturing. AnyShape leverages additive manufacturing for aerospace to produce the most lightweight yet durable components, reducing fuel consumption and improving overall flight performance. Our innovative additive manufacturing technologies allow us to manufacture complex geometries that were previously unattainable with traditional methods, such as structural supports and advanced fuel systems; keeping your aerospace project soaring.
Championing green innovation in aerospace
As well as delivering unparalleled performance, AnyShape’s additive manufacturing processes contribute to a more sustainable aerospace industry. Metal 3D printing for aerospace drastically reduces waste by utilizing only the material required for each component. Our processes allow for digital inventory and on-demand production, minimizing the need for excess stock and reducing the overall carbon footprint associated with aerospace production.


AnyShape is the supplier I use the most for tooling as they lead the way in terms of both part quality and AM knowledge and capability. Over the past four years AnyShape have always met my needs and added value to all my projects
Trusted by engineers worldwide
-
How is 3D printing used in aerospace?
3D printing is utilized throughout the aerospace industry for prototyping, tooling, and manufacturing mission-critical components. This innovative manufacturing method facilitates faster iteration, complex geometries, and reduced material waste, making it ideal within both the research and production phases.
-
Is it possible to 3D print a rocket?
While 3D printed rockets are yet to become the norm, significant strides have been made. Back in 2023, NASA successfully launched a rocket made entirely of 3D printed parts, known as the Terran-1. This milestone proves that additive manufacturing is capable of producing fully functional 3D printed components for aerospace.
-
What are the advantages of 3D printing in aerospace?
The biggest benefit of additive manufacturing for aerospace is its ability to produce complex components that were not previously possible with traditional tooling and manufacturing techniques. It speeds up development, minimizes material costs, and streamlines supply chains, making it an ideal choice for innovation in space technology.
-
What are the disadvantages of 3D printing in aerospace?
While 3D metal printing for aerospace has many advantages, there are some challenges to consider. Every component is limited by the size of the printer, making larger components more complex to print. For larger production runs, 3D printing can be more expensive compared to traditional mass production methods, and additional processing may also be required for surface finishing.